Transforming Data into Insight: The Impact of Visualization in Analytics
Is the complexity of your data making it hard to understand and analyze? Here’s a fact – data visualization is transforming the way we utilize large datasets. In this article, we’ll delve into how data visualization simplifies complex information, enabling clear understanding and effective decision-making.
Get ready to explore the exciting world of visualized data!
Key Takeaways
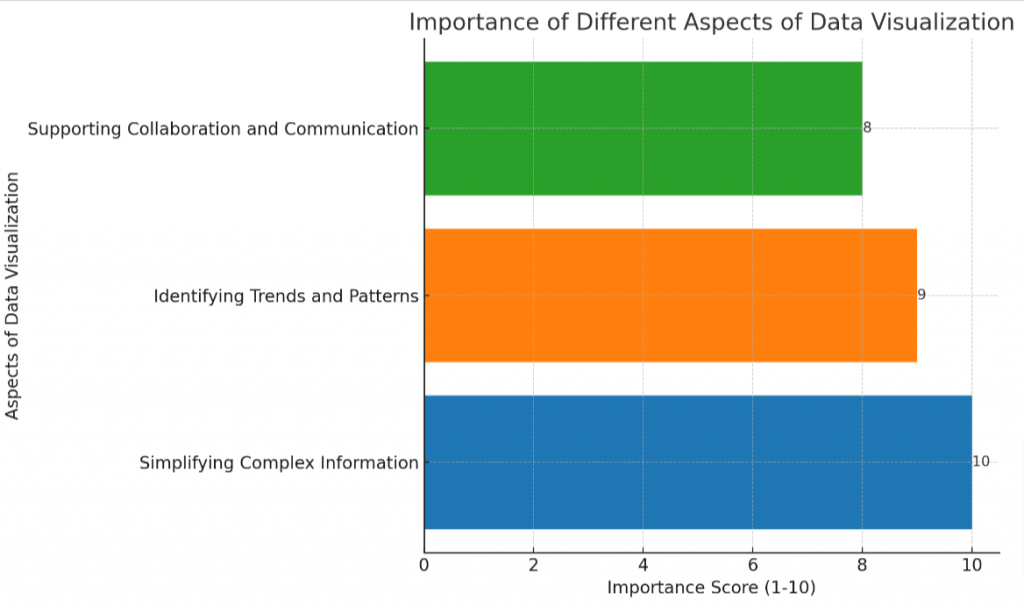
- Data visualization simplifies complex information, making it easier to understand and analyze.
- It helps in identifying trends and patterns within large datasets, enabling businesses to make data – driven decisions.
- Data visualization supports collaboration and communication by creating a common language that facilitates effective discussions around data insights.
The Importance of Data Visualization in Analytics
Data visualization plays a crucial role in analytics by making complex data easier to understand, identifying trends and patterns, facilitating data-driven decision making, and supporting collaboration and communication.
Making complex data easier to understand
Data visualization is the game-changer in efficiently managing and comprehending complex data. It works by converting complicated, intricate datasets into visually appealing and more digestible formats such as charts, graphs, or maps.
This graphical representation of information allows us to perceive and interpret difficult patterns, trends, or outliers within data at a glance. By enabling instant understanding of multifaceted information sets through intuitive depictions, it becomes an effective tool for decision-makers who require quick insight to form strategic initiatives.
Thus making sense of large volumes of intricate datasets falls right into the wheelhouse of impactful data visualization techniques.
Identifying trends and patterns
Data visualization plays a critical role in spotting trends and patterns. Large data sets can become unwieldy, hiding important insights within their numerous columns and rows. Data visualization techniques like heat maps, line charts or scatter plots transform this raw information into visual formats that are easier to understand.
This transformation helps businesses uncover patterns in data that might have otherwise gone unnoticed.
Identifying trends and patterns doesn’t just spotlight current business situations; it also paves the way for predictive analytics. By visualizing past and present data, companies can forecast future scenarios with remarkable accuracy.
This foresight enables proactive decision-making which is key in today’s fast-paced business environment. Be it sales projections, customer behavior analysis or operational efficiency metrics; identifying trends through data visualization often spells the difference between staying ahead of the curve or falling behind competition.
Facilitating data-driven decision making
Data visualization is a key player in facilitating data-driven decision making. It transforms complex datasets into easy-to-understand visual presentations – be it charts, graphs or maps – aiding individuals and businesses to identify trends and patterns in their data.
This aids analysts, executives, and stakeholders effectively make more informed decisions based on these insights. From understanding customer behavior for better product development to identifying changes in customer needs or preferences, the applications are vast.
Businesses that harness the power of data visualization are often ahead because it presents them with a clear vantage point in their decision-making processes.
Supporting collaboration and communication
Data visualization creates a common language enabling teams to collaborate and communicate effectively. It breaks down complex information into easily digestible visuals, facilitating discussions around data-driven insights.
By picturing the data’s story, team members from diverse backgrounds can contribute valuable input and foster cohesive decision-making processes. Leveraging data visualization tools helps eliminate misunderstandings by providing clear visual representations of trends and patterns that text-based data could complicate or obscure.
Through such effective communication, organizations can align their strategies much more efficiently. These tools are not just advantageous for internal use but also boost clarity in presentations to potential partners or shareholders helping them grasp intricate ideas swiftly.
The Interplay Between Big Data and Data Visualization
Data visualization and big data go hand in hand, as they complement each other perfectly to unlock valuable insights. Big data refers to the vast amounts of information that companies collect from various sources, such as social media, sensors, and customer interactions.
However, raw big data can be overwhelming and difficult to interpret. This is where data visualization comes into play. By visually representing complex datasets through graphs, charts, and diagrams, data visualization simplifies the understanding of big data.
It allows analysts to identify trends, patterns, and outliers that may have gone unnoticed in raw form. With the help of intuitive visualizations, organizations can make informed decisions based on a clear interpretation of their big data.
The interplay between big data and data visualization is crucial for businesses looking to leverage the power of analytics effectively. Visualizing large datasets not only makes them more digestible but also enhances collaboration within teams by promoting better communication among stakeholders.
With the aid of interactive dashboards and visual representations generated by powerful tools like Tableau or Zoho Reports (among others), decision-makers can gain deeper insights into their organization’s performance across different departments or business sectors.
Common Types of Data Visualization
Line charts, area charts, scatter plots, treemaps, and population pyramids are some common types of data visualization used in analytics.
Line charts
Line charts are a commonly used type of data visualization in analytics. They are effective in displaying trends and patterns over time, making them particularly useful for visualizing continuous data or data that changes over a specific time period.
Line charts consist of a series of data points connected by straight lines, allowing for easy comparison between different data series. By adding multiple lines or using different colors or patterns, multiple data series can be compared on a line chart.
Overall, line charts provide a clear and concise way to represent and analyze data trends over time.
Area charts
Area charts are a common type of data visualization used to show trends over time. They are particularly effective in comparing multiple categories or data series within a dataset.
The filled area in an area chart represents the magnitude or proportion of the data being represented, making it easy to see changes and identify patterns. Additionally, area charts can help highlight outliers or anomalies in the data.
With their intuitive visuals, area charts provide a clear and concise way to understand and analyze data trends over time.
Scatter plots
Scatter plots are a powerful data visualization tool that displays the relationship between two variables. By plotting each data point on a graph, scatter plots can show whether there is a positive or negative correlation between the variables.
They are particularly useful for identifying patterns or trends in data, allowing us to see if there is any relationship between the variables being studied. Additionally, scatter plots can help us identify outliers or anomalies in the data, as they stand out from the general pattern of points on the graph.
To enhance scatter plots further, we can include additional visual elements that represent other dimensions of the data, such as color or size.
Treemaps
Treemaps are graphical representations that use nested rectangles to display hierarchical data. They are particularly useful when visualizing large datasets with hierarchical structures, such as organizational hierarchies or file systems.
With treemaps, both categorical and quantitative data can be displayed, where the size and color of the rectangles represent different variables or attributes. This allows users to quickly identify patterns and relationships within the data, as well as compare the relative sizes and proportions of different categories or groups.
Treemaps find applications in various fields including finance, market research, and supply chain management for visualizing complex datasets.
Population pyramids
Population pyramids visually represent the age and gender distribution of a population. They provide valuable insights into population trends, such as aging populations or population growth.
Typically used in demographic analysis, urban planning, and healthcare planning, population pyramids allow analysts to easily identify imbalances within a population, such as gender disparities or age disparities.
By visualizing data through pyramids, potential areas of concern can also be identified, like a shrinking workforce or an aging population.
Practical Applications of Data Visualization
Data visualization plays a crucial role in various industries including sales and marketing, politics, healthcare, science, finance, logistics, data science, and research.
Sales and Marketing
Data visualization plays a critical role in sales and marketing by helping businesses analyze customer behavior and make informed decisions. It allows organizations to understand the impact of their marketing efforts on web traffic and revenue.
By visually representing data, such as through histogram plots, scatter plots, and pie charts, data visualization enables marketers to identify patterns and trends that can guide their strategies.
To support these efforts, there are top data visualization tools available for sales and marketing professionals like Tableau, Looker, Zoho Analytics, and Microsoft Power BI. These tools empower sales teams to present data in a clear and compelling way to stakeholders, ultimately driving more effective decision-making processes.
Politics
Data visualization plays a crucial role in politics. It helps individuals and organizations understand complex political data more easily. Through the use of charts, graphs, and maps, data visualization allows for the effective presentation of political information.
This makes it easier for people to analyze and interpret political trends, patterns, and relationships. Furthermore, data visualization supports collaboration and communication within political organizations by providing a clear visual representation of important data points.
With the help of data visualization tools like Tableau or Google Charts, politicians can make informed decisions based on reliable data analysis.
In addition to improving understanding and decision-making processes in politics, data visualization has practical applications as well. For example, during election campaigns or policy debates, visualizing voter demographics through population pyramids or choropleth maps can provide valuable insights into voting patterns across different regions.
Healthcare
Data visualization plays a crucial role in the healthcare industry by helping organizations effectively utilize large datasets and make informed decisions. With the help of visual representations, complex healthcare data becomes easier to understand, allowing healthcare professionals to identify patterns and trends that may have gone unnoticed in raw data sets.

By enabling data-driven decision making, data visualization supports better patient care, improved diagnosis accuracy, and more efficient resource allocation within healthcare organizations.
It empowers stakeholders to interpret and communicate findings efficiently, leading to better collaboration among teams and ultimately improving overall healthcare outcomes.
Science
Science relies heavily on data analysis and visualization to make sense of complex information. By using visual representations, scientists can easily identify trends and patterns in their research findings.
This helps them gain a deeper understanding of their subject matter and make data-driven decisions. Whether it’s analyzing the results of an experiment or mapping out the spread of a virus, data visualization plays a crucial role in scientific research.
It allows scientists to communicate their findings effectively and collaborate with other researchers in order to advance knowledge and drive innovation.
Finance
Data visualization plays a crucial role in the field of finance. It enables professionals to make more informed decisions by converting complex financial data into visually appealing and intuitive representations.
By using various data visualization techniques such as line charts, bar charts, and heat maps, finance professionals can identify trends and patterns in the data that may not be immediately apparent through raw numbers alone.
This facilitates data-driven decision making, allowing organizations to make strategic choices based on actionable insights. Additionally, data visualization supports collaboration and communication within finance teams, ensuring that everyone has a clear understanding of the information presented and can work together effectively towards common goals.
Logistics
Data visualization plays a crucial role in the field of logistics. By employing data visualization techniques, businesses in the logistics sector can gain valuable insights and identify patterns that may have previously gone unnoticed.
This allows them to better understand and analyze their performance across different aspects of their operations. Moreover, data visualization supports collaboration and communication within organizations, enabling teams to work together more efficiently towards common goals.
With the help of data visualization, businesses can make informed decisions about resource allocation in order to improve efficiency and optimize operations in the logistics sector.
Data Science and Research
Data science and research rely heavily on data visualization to uncover patterns, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. Visualizing large data sets allows analysts to explore the relationships between variables and detect outliers or unusual distributions.
It is an essential tool for presenting results and communicating findings within organizations. Robust computer systems are necessary for effectively visualizing big data in research settings.
Data Visualization Techniques
Data Visualization Techniques include popular tools such as pie charts, bar charts, histograms, and Gantt charts. These techniques help present data in a visually engaging way, making it easier for audiences to understand complex information.
Read on to explore the various techniques and how they can enhance your data analysis skills.
Pie Chart
Pie charts are circular graphs that represent data using sectors. Each sector of a pie chart is proportional to the data it represents. These charts effectively display proportions and percentages of different categories within a whole.
They are commonly used in business analytics to visualize market share, sales distribution, and customer segmentation. Pie charts are easily understood and interpreted, making them valuable for displaying categorical data.
Bar Chart
Bar charts play a crucial role in data visualization for analytics. These charts use rectangular bars to represent different variables, making it easy to understand the relationship between them.
Bar charts are especially useful for analyzing and comparing categorical data, such as sales figures or department performance. They allow us to identify trends, spot patterns, and even highlight outliers in the data.
With their simplicity and clarity, bar charts provide valuable insights that aid decision-making processes.
The effectiveness of bar charts lies in their ability to present information clearly and concisely. Their visual representation helps users interpret data quickly, enabling faster analysis.
Histogram
Histograms are a powerful tool for visualizing numerical data. They divide the data into intervals or bins and show the frequency of data points in each bin. This helps analysts understand the distribution of the data and identify patterns and trends.
The shape of a histogram can provide insights into whether the distribution is symmetric, skewed, or bimodal. Additionally, histograms can be used to spot outliers or unusual data points that may require further investigation.
By examining the width of the bins and the height of the bars, analysts can gain an understanding of the range and spread of the data.
Gantt Chart
Gantt charts are visual representations of project timelines. They play a crucial role in tracking project progress and identifying any bottlenecks along the way. By providing a clear overview of tasks and their corresponding timelines, Gantt charts help project managers manage resources effectively and allocate them where they are needed most.
One of the key benefits of Gantt charts is that they allow for easy identification of task dependencies, enabling teams to understand how each task relates to others in the larger project.
This makes Gantt charts particularly valuable for visualizing complex projects with multiple tasks and dependencies. Overall, Gantt charts provide an efficient way to manage projects and ensure that all tasks are completed on time.
Heat Map
Heat maps are a powerful data visualization tool that uses color gradients to represent the intensity or density of data points in a specific area. They are particularly useful for visualizing large datasets and identifying patterns and trends within the data.
Heat maps can help businesses gain insights into customer behavior by showing hotspots or areas of high activity, allowing them to optimize their performance accordingly. In geographic analysis, heat maps can show the distribution of data across different regions or areas, making them invaluable for understanding spatial relationships.
Additionally, heat maps are widely used to analyze website traffic, social media engagement, and user interactions, providing valuable insights into audience behavior and preferences.
Box and Whisker Plot
A Box and Whisker plot is a powerful data visualization tool that provides a concise summary of a dataset. It shows the minimum, maximum, median, and quartiles of the data in an easy-to-understand format.
By displaying these key statistics, it helps identify any outliers and gives insights into the spread and skewness of the data.
One of the main advantages of using Box and Whisker plots is their ability to compare multiple datasets or groups effectively. They show the range and variability within each dataset, making it easy to detect differences or similarities between them.
Because of this, Box and Whisker plots are commonly used in exploratory data analysis and hypothesis testing.
Furthermore, Box and Whisker plots are particularly useful for displaying non-normally distributed or multimodal data. They provide a clear visual representation of how the values are distributed across quartiles.
Waterfall Chart
Waterfall charts are a valuable tool in analytics for visually representing changes and comparing values over time. They are particularly useful for showing the cumulative effect of positive and negative values on a starting value.
Each bar in a waterfall chart represents a specific category or period, with the length of the bars indicating the change in value. These charts are commonly used in financial analysis to track revenue, expenses, and net profit.
In addition, they can be utilized to analyze sales performance, project budgets, and cash flow. With their clear and intuitive format, waterfall charts make it easy to understand complex data and identify trends at a glance.
Top Data Visualization Tools
Some of the top data visualization tools include Tableau, Dundas BI, Jupyter Notebook, Zoho Reports, and Google Charts.
Tableau
Tableau is a highly regarded data visualization tool that provides users with a range of powerful features. It is widely recognized as one of the top tools in the market for creating visually appealing and interactive dashboards.

Additionally, Tableau offers a free version for personal use, making it accessible to individuals who want to explore and analyze their data without any upfront cost. With its user-friendly interface and robust capabilities, Tableau has become an essential tool for professionals in various industries seeking to gain insights from their data through visualizations.
Dundas BI
Dundas BI is a leading data visualization tool in the field of analytics. It empowers businesses to make sense of large datasets by presenting them through visually appealing charts, graphs, and maps.
With Dundas BI, companies can uncover patterns in their data that may have been difficult to spot in raw formats. This enables more informed decision-making and helps businesses stay ahead in today’s data-driven world.
Additionally, complex data becomes easier to understand with Dundas BI’s intuitive and user-friendly interface, making it accessible to users at all levels of expertise.
Jupyter Notebook
Jupyter Notebook is a powerful tool that allows users to create various types of visualizations, such as charts, graphs, maps, and interactive dashboards. It seamlessly integrates with popular data visualization libraries like Matplotlib, Seaborn, and Plotly.
With Jupyter Notebook, large datasets can be handled effectively, providing real-time exploration and visualization capabilities. What makes Jupyter Notebook stand out is its accessibility to both technical and non-technical users.
By using visual representations of data through Jupyter Notebook, the understanding and interpretation of complex information are greatly enhanced.
Zoho Reports
Zoho Reports is a highly regarded data visualization tool that helps businesses make the most of their large datasets. It simplifies complex data by transforming it into visually appealing charts, graphs, and maps.
With Zoho Reports, companies can easily understand and analyze their data, supporting informed decision-making. This powerful tool, along with other top data visualization tools in the market, plays a crucial role in analytics by presenting information in an intuitive and visually stimulating format.
Google Charts
Google Charts is a highly popular and widely used data visualization tool in the field of analytics. It plays a crucial role in helping businesses and researchers understand complex data sets by identifying trends and patterns that may not be easily noticeable in raw data.
With its user-friendly interface and powerful features, Google Charts enables professionals across different industries such as sales, marketing, finance, and logistics to visualize and analyze large amounts of data effectively.
Furthermore, data scientists and researchers rely on Google Charts to gain insights from their datasets through visual representations. Its popularity has soared due to the increasing demand for analyzing big data projects efficiently.
Conclusion
Data visualization plays a crucial role in analytics by making complex data easier to understand, identifying trends and patterns, facilitating data-driven decision-making, and supporting collaboration and communication.
With the increasing importance of big data, visualization tools like Tableau, Dundas BI, Jupyter Notebook, Zoho Reports, and Google Charts are invaluable for transforming raw data into visually appealing representations.
In today’s data-driven world, effective data visualization is essential for gaining meaningful insights and making informed decisions.

