Staying Ahead of the Curve: Exploring New Horizons with Upcoming Social Media Platforms
Are you grappling with understanding the rapidly evolving landscape of remote work legislation? The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed a seismic shift towards remote and hybrid working models, leading to a surge in new legislation worldwide.
This blog unravels the intricacies of those policies, their impact on industries, and future trends we can anticipate. Get ready to dive deep into this critical facet of our increasingly digital work world – let’s get started!
Key Takeaways
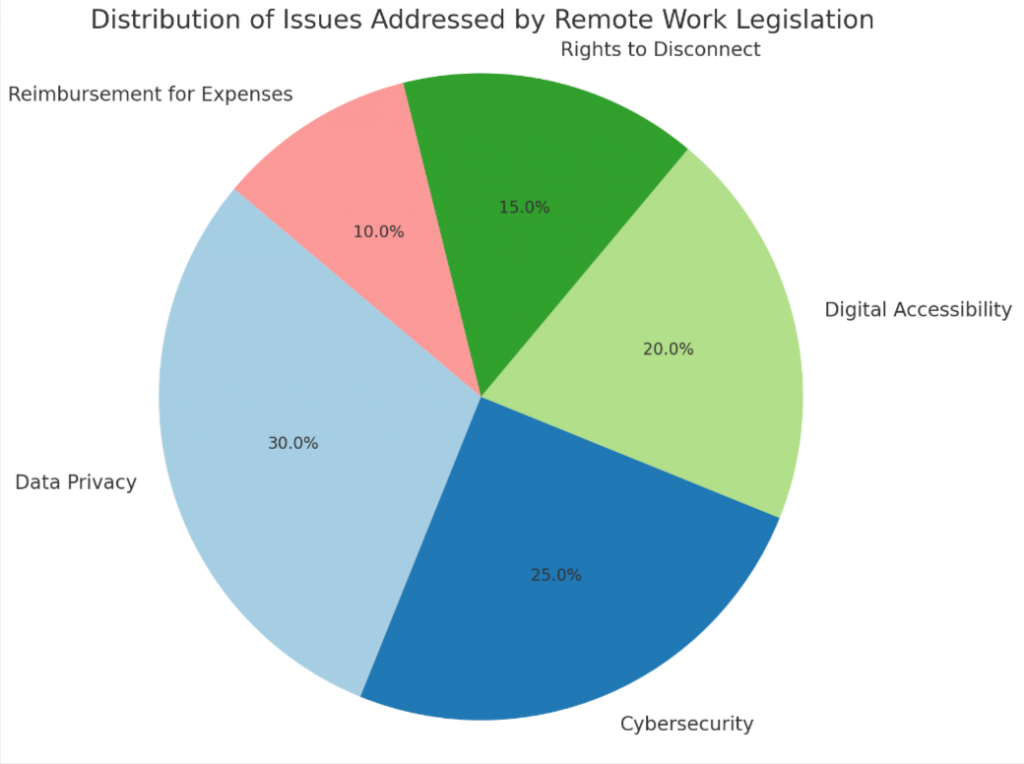
- Remote work legislation is emerging worldwide to address the demands of the changing workforce.
- It includes provisions such as written agreements, rights to disconnect, and reimbursement for teleworking expenses.
- Companies play a crucial role in shaping future remote work legislation by providing necessary resources and support for effective communication and collaboration.
- Technology will continue to influence remote work legislation, addressing issues like data privacy, cybersecurity, and digital accessibility.
Understanding Remote Work Legislation
As our society continues to embrace the digital age, we must also adapt our laws to address new trends. Remote work legislation is emerging worldwide as an effort to meet this demand.
Countries such as Angola, Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Chile and many more have already implemented measures for protecting remote workers. These laws typically cover aspects such as written agreements between employers and employees about working remotely.
This includes rights of employees around disconnection after work hours and reimbursement of expenses related to remote work setup. Some countries even offer tax-free allowances specifically intended for home-based workers or principles that favor certain demographics like individuals with disabilities or those nurturing young children at home.
Other legal mechanics revolve around providing necessary tools required by a worker in their job function while located off-site.
No one-size-fits-all approach exists when it comes down to governing remotely done jobs due its diverse nature on a global scale; yet trend indicates an inclusive focus by making sure everyone involved in remote work are taken into account through these legislations.
This occurs by looking specifically into elements such as flexible scheduling along with health and safety information dissemination which help establish a balanced view on maintaining productivity without compromising well-being amongst remote workforce employed by companies across variegated industries.
Recent Developments in Remote Work Legislation Worldwide
Countries around the globe are recognizing the importance of remote work and implementing legislative measures to accommodate this new workforce.
- Angola ushered in teleworking legislation that took effect in March 2022, a significant step towards remote work regulation.
- Argentina set a precedent with its introduction of a teleworking law in April 2021, including rights for workers to disconnect and reimbursement for expenses related to working remotely.
- Australia passed the “Secure Jobs, Better Pay” Act in December 2022, extending flexible work arrangements and dispute handling powers to accommodate remote employees.
- In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, Belgium offered tax relief by introducing a tax-free work from home allowance as a permanent measure.
- Brazil adopted electronic timekeeping systems for remote workers through a landmark legislation and expanded labor laws to cover those working remotely.
- Canada made amendments to the Canada Labour Code in July 2023, requiring employers to reimburse employees for work-related expenses incurred due to remote working.
The Impact of Remote Work on Different Industries
Remote work has led to the rise of hybrid work models, transformed urban economies, and shifted organizational practices. Discover how remote work is shaping different industries in our blog.
The Rise of Hybrid Work Models
Hybrid work models, a blend of in-person and remote work, have seen significant growth in recent years. Encouraged by the flexibility they offer, many companies and workers have embraced these models during the COVID-19 pandemic.
This shift has been fueled not only by necessity but also by the potential for greater productivity and improved work-life balance. The prediction is that over 20 percent of employees could successfully work from home three to five days a week without losing effectiveness – that’s a major game-changer!
Even more remarkable is the potential impact on office spaces: with one-third of US chief operating officers considering reducing their physical footprint post-pandemic, we might see an increased office vacancy rate up to 19.4 percent as soon as the end of 2022.
The Effect on Urban Economies
Urban economies undergo significant changes in the era of remote work. As companies reduce office space, the ripple effect touches restaurants, bars, and retail stores that previously served office workers.
This decline in business activity could lead to a decrease in tax revenues for state and local governments. The looming rise of the U.S office vacancy rate to 19.4% by end of 2022 reflects this reality vividly.
With one-third of U.S chief operating officers planning on reducing physical workspace, we are looking at an era where major downtown districts transform dramatically from bustling centers of commerce into quieter neighborhoods with fewer daily visitors.
The Shift in Organizational Practices
Organizational practices have undergone a significant shift due to the rise of remote work. Companies are reevaluating their traditional office setups and embracing more flexible arrangements.
With the implementation of remote work legislation, organizations have had to adapt by providing remote workers with the necessary tools and support for effective communication and collaboration.
This shift has also led to a greater emphasis on results rather than physical presence, as companies focus on measuring productivity and outcomes rather than hours spent in the office.
Future Trends in Remote Work Legislation
Companies will play a significant role in shaping remote work legislation, potentially leading to increased worker rights and the influence of technology on future legislation.
The Role of Companies in Shaping Legislation
Companies play a crucial role in shaping legislation related to the future of remote work. They have the responsibility to provide necessary resources, tools, and equipment to enable their employees to effectively work from home.
Remote work legislation includes requirements for written agreements, rights to disconnect, reimbursement of expenses, and provision of necessary tools and equipment. It also covers health and safety policies, personal data protection, and compliance with working hour regulations.
Moreover, companies’ decisions to reduce office space can have an impact on local businesses and tax revenues.
The Potential for Increased Worker Rights
Remote work legislation has the potential to significantly enhance worker rights. These laws often include provisions that protect remote workers, such as the right to disconnect and flexible working schedules.
They also address issues like reimbursement for teleworking-related expenses and access to necessary tools and equipment. Additionally, some countries have extended the right to request flexible work arrangements, empowering employees with more control over their work-life balance.
By implementing robust remote work legislation, governments can ensure that workers are treated fairly and provided with the necessary support and protections in this evolving work landscape.
The Influence of Technology on Future Legislation
Technology is exerting a significant influence on future legislation concerning remote work. As the reliance on technology continues to grow, lawmakers are recognizing the need for updated regulations that address the unique challenges and opportunities presented by remote work.
Technology has facilitated the rise of remote work and enabled individuals to connect and collaborate across geographical boundaries. It has also highlighted issues such as data privacy, cybersecurity, and digital accessibility that must be addressed in future legislation.
With advancements in communication software, project management tools, and collaboration platforms, it is crucial for legislation to keep pace with technological developments to ensure fair treatment of remote workers and protect their rights.
The Challenges and Opportunities of Remote Work Legislation
Balancing employee rights with employer needs, adapting to technological changes, and overcoming legal and regulatory hurdles present both challenges and opportunities in remote work legislation.
Balancing Employee Rights with Employer Needs
Remote work legislation aims to strike a delicate balance between protecting employee rights and addressing the needs of employers. It recognizes the importance of ensuring fair treatment, workplace safety, and equal opportunities for remote workers while also considering the operational requirements of businesses.
This involves implementing measures such as providing tax-free allowances, extending remote work options for vulnerable employees and parents with young children, and establishing regulations to ensure occupational health and safety requirements are met.
By finding this equilibrium, remote work legislation creates a framework that supports both employees and employers in navigating the challenges and opportunities presented by remote work.
Adapting to Technological Changes
Remote work legislation must adapt to the technological changes brought about by the rise of remote work. As companies and employees increasingly rely on technology to facilitate remote collaboration, it is crucial for legislation to address issues such as data protection, cybersecurity, and digital infrastructure.
With more people working remotely, there is a greater need for regulations that ensure fair treatment of workers in terms of access to necessary resources and equipment. Additionally, legislation should consider the impact of technology on work-life balance, including provisions for managing digital overload and promoting the right to disconnect from work-related communications outside of regular working hours.
Embracing technological advancements can foster a seamless transition towards a future where remote work is both efficient and equitable for all parties involved.
Overcoming Legal and Regulatory Hurdles
To successfully implement remote work legislation, there are several legal and regulatory hurdles that need to be overcome. These include:
- Ensuring compliance with existing labor laws and regulations, such as working hours legislation and occupational health and safety requirements.
- Addressing logistical and structural legal challenges, such as determining the rights and responsibilities of on-site workers versus remote workers.
- Adapting collective bargaining agreements to account for remote work arrangements and the changing nature of work.
- Establishing clear guidelines and procedures for remote work, including teleworking agreements, written agreements between employers and employees, and reimbursement of expenses.
- Determining employer liability for remote work – related injuries or accidents.
- Guaranteeing equal treatment for all employees, regardless of their work location.
- Collaborating with relevant government agencies, such as the Federal Ministry of Labor, Employment, and Social Security (FMLESS) in Argentina or the Fair Work Commission (FWC) in Australia.
Case Studies of Remote Work Legislation
Explore real-life examples of remote work legislation in action, including California’s Caste Discrimination Bill, Amazon’s Wage Increase, and UAW Strike Demands. Discover the impact these cases have had on shaping remote work legislation and its future.
California’s Caste Discrimination Bill
California has introduced a Caste Discrimination Bill that aims to address discrimination based on caste. The bill is one of the case studies on remote work legislation, highlighting the importance of creating an inclusive and equitable work environment.
This legislation recognizes that all individuals should be treated fairly, regardless of their caste background. It reflects California’s commitment to promoting diversity and preventing discrimination in the workplace.
The bill provides additional protections for employees who may face discrimination based on their caste status, ensuring equal opportunities for everyone in the workforce. By addressing this issue head-on, California sets an example for other jurisdictions to follow in promoting equality and inclusivity in remote work settings.
Amazon’s Wage Increase
Amazon’s wage increase is a notable case study in remote work legislation and offers insights into the future of this growing trend. While specific details of the wage increase are not mentioned, this development showcases how companies are adapting to the changing dynamics of remote work.
It also highlights the potential for increased worker rights as organizations recognize the importance of fair compensation for remote employees. This case study serves as an example of how companies can shape legislation and contribute to creating a more equitable and sustainable remote work environment.
UAW Strike Demands
The UAW union recently went on strike to demand better working conditions and higher wages for its members. Workers were seeking improved benefits, including increased healthcare coverage and retirement plans.
They also pushed for stronger job security measures to protect against layoffs and outsourcing. The strike drew attention to the importance of fair compensation and workplace rights in the remote work era, emphasizing the need for companies to prioritize the well-being of their employees.
The Pros and Cons of Remote Work Legislation
Remote work legislation offers numerous benefits for employees, including increased flexibility, improved work-life balance, reduced commuting time and costs, and access to a wider pool of talent.
However, it also presents challenges for employers such as reduced face-to-face communication, feelings of isolation and disconnection among remote workers, difficulty maintaining work-life boundaries, and the need to rely heavily on technology.
Benefits for Employees
Remote work legislation offers several benefits for employees. It provides them with increased flexibility, allowing them to have a better work-life balance. By working remotely, employees can save time and money on commuting, which reduces stress and improves their overall well-being.
Additionally, remote work allows access to a wider pool of talent, as geographical limitations are no longer a barrier. This can lead to more diverse teams and increased creativity within organizations.
Furthermore, remote work legislation prioritizes the rights of caregivers in the workplace, making it easier for them to manage their professional responsibilities while also attending to family needs.
Challenges for Employers
Employers face several challenges when it comes to remote work legislation. Firstly, they may be required to reimburse teleworking-related expenses for their remote employees, which can add financial strain.
Additionally, employers are responsible for providing the necessary tools and equipment for remote work, ensuring that employees have everything they need to perform their tasks effectively.
Another challenge is establishing the right for employees to disconnect after working hours, as this can blur the boundaries between work and personal life. Furthermore, employers must comply with health and safety regulations and inform employees about health and safety policies to ensure a safe working environment.
Frequently Asked Questions about Remote Work Legislation
Remote work legislation can be complex and may raise many questions. Here are some frequently asked questions about remote work legislation:
Q: What countries have implemented remote work legislation?
A: Angola, Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, and the Czech Republic.
Q: What are some key provisions of remote work legislation?
A: Written agreements, reimbursement of expenses, and rights to disconnect.
Q: When does Angola’s remote work legislation take effect?
A: March 20, 2022.
Q: What provisions are included in Argentina’s teleworking law?
A: Written agreements, respect for employees’ right to disconnect, and reimbursement for teleworking – related expenses.
Q: What is Australia’s “Secure Jobs, Better Pay” Act?
A: It expands the right to request flexible work arrangements and grants powers to handle disputes to the Fair Work Commission.
Q: What measures has Belgium introduced regarding remote work?
A: A tax – free work from home allowance and a requirement for employers with 20 employees or more to establish the right for employees to disconnect after working hours.
Conclusion
Remote work legislation is rapidly evolving to meet the demands of a changing workforce. Countries around the world are recognizing the need for written agreements, employee rights to disconnect, and reimbursement for teleworking expenses.
Companies also play an important role in shaping future legislation as they adapt their practices to accommodate remote work. As technology continues to advance, it will influence and shape the future of remote work legislation even further.
The challenges and opportunities that come with remote work legislation will continue to be addressed as we navigate this new landscape.

