Unlocking Business Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to KPIs
Looking to enhance business performance, but not sure where to start? You’re not alone. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) offer an effective solution, providing measurable and quantifiable metrics that help businesses make data-driven decisions.
This comprehensive guide will introduce you to the concept of KPIs, their importance, how they differ from regular metrics and more – all in a simplified language that’s easy for anyone to understand.
Ready for better decision-making? Let’s dive right in!
Key Takeaways
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable measures that track progress towards specific objectives in various areas within a business.
- KPIs differ from regular metrics as they focus on factors with substantial impact on business results and provide targets and detailed information.
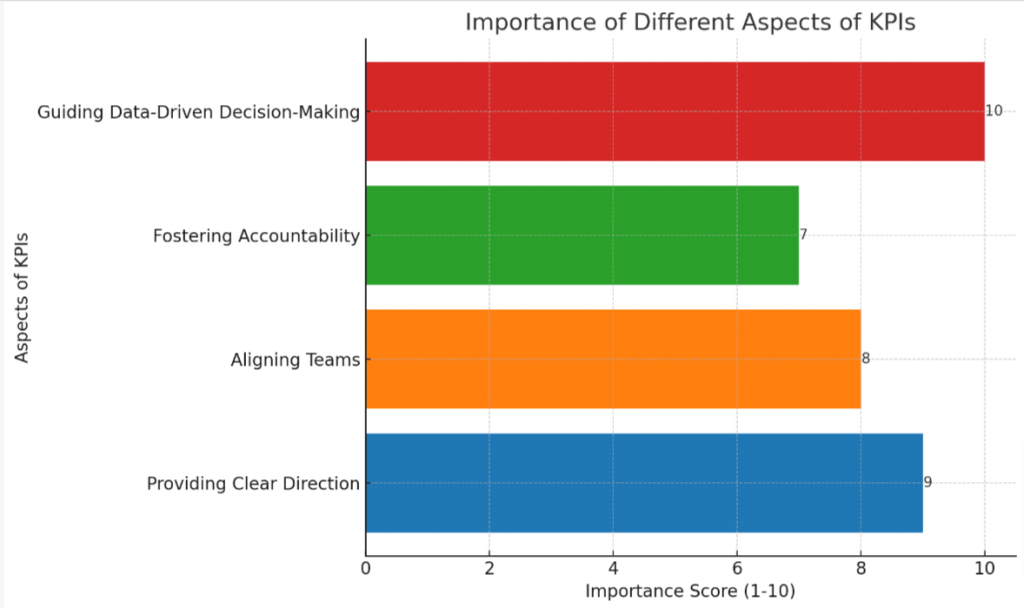
- KPIs are vital for driving business success, providing clear direction, aligning teams, fostering accountability, and guiding data-driven decision-making processes.
- Different types of KPIs include sales KPIs, marketing KPIs, financial KPIs, operational KPIs, and customer KPIs.
Understanding KPIs: What are Key Performance Indicators?
Key Performance Indicators, or KPIs for short, are quantifiable measures of performance. They track progress over time towards specific objectives in various areas within a business.
For instance, companies can employ these data-driven tools to monitor trends, measure efficiency, and determine how well they’re attaining their strategic goals.
These indicators offer critical insights that guide individuals and teams in decision-making processes; hence pushing the needle forward on strategic outcomes. KPIs differ significantly from everyday metrics as they focus primarily on factors with substantial impact on business results.
Their ability to provide targets along with detailed information make them instrumental in keeping teams aligned while fostering accountability across an organization’s operations.
The Distinction: KPI Meaning vs Metrics Meaning
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct roles in business performance tracking. KPIs provide a lens to the organization’s strategic priorities.
They are quantifiable measures of how successfully an institution is meeting its key objectives or goals over time. Therefore, the main role of KPIs pivots around boosting organizational growth and success.
On the other hand, Metrics exist to support these KPIs by providing context for everyday business operations. Metrics play a particular role in measuring specific routine activities that may directly or indirectly impact key performance indicators’ progress.
While both KPIs and metrics serve as tools for evaluation, differentiation comes with their usage. A metric examines any part of a process; conversely, a Key Performance Indicator is consistently an outcome-based measure linked tightly to strategic business outcomes.
Further clarification reveals that all KPI’s can be considered as metrics but not all metrics qualify as Key Performance Indicators because only those metrics most critical to achieving vital organizational targets should earn ‘KPI’ status.
The Significance of KPIs: Why Are KPIs Important?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are vital in driving business success. They serve as quantifiable measures that provide targets, milestones, and insights for tracking progress towards specific objectives.
Without KPIs, a company is essentially flying blind, without any clear sense of direction or understanding of its performance.
Moreover, KPIs play an important role throughout all areas of a business from finance to sales to human resources and marketing. These versatile tools help keep teams aligned by providing a constant measure of organizational health.
It ensures every team member understands what’s at stake and their role in the bigger picture.
Furthermore, they hold teams accountable for their actions by clearly outlining what needs to be achieved. Accountability increases efficiency and productivity while pushing individuals to strive harder toward achieving strategic outcomes.
With proper utilization of KPIs, organizations can actively engage in data-driven decision-making processes ensuring optimal business performance optimization. Strategic KPIs guide organizations towards appropriate direction aligning with overall business strategy.
Various Types of KPIs
Different types of KPIs include sales KPIs, marketing KPIs, financial KPIs, operational KPIs, and customer KPIs.
Sales KPIs
Sales KPIs serve as a valuable tool for businesses striving to meet and surpass their sales goals. These specific performance indicators reveal the health of your sales processes, shedding light on trends in revenue, growth rates, customer acquisition efforts, and conversion success.
The power of Sales KPIs stems from their ability to provide clear-cut targets that articulate how well the business is performing against its sales objectives. On top of this, individual salespeople along with entire teams can be assessed based on these metrics, bringing insights into performances and identifying room for improvement.
Furthermore, they stimulate data-driven decision-making leading to enhanced strategies that boost overall sales results. From startups to big enterprises alike, understanding and implementing effective Sales KPIs are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in today’s market landscape.
Marketing KPIs
Marketing KPIs are quantifiable measures used to track performance in marketing objectives. These KPIs provide targets, milestones, and insights that help marketers make better decisions and gauge their progress.
By monitoring marketing KPIs, teams can align their efforts, assess the health of their marketing organization, and hold themselves accountable for results. There are different types of marketing KPIs: strategic KPIs measure progress towards marketing goals, operational KPIs evaluate shorter-term performance, and functional unit KPIs are tied to specific marketing functions.
Some examples of marketing KPIs include measuring marketing qualified leads, return on ad spend, and conversion rates.
Financial KPIs
Financial KPIs are essential for tracking and analyzing an organization’s financial progress. These indicators provide valuable insights into the company’s performance and help make data-driven decisions.
Examples of financial KPIs include revenue growth rate, net profit margin, cash flow, and expenses. By monitoring these metrics, businesses can assess their profitability, manage cash effectively, and evaluate overall financial health.
It is crucial for finance departments as well as other functional units like sales, marketing, customer service, and IT to utilize relevant financial KPIs that align with their specific objectives.
Operational KPIs
Operational KPIs are a key component in measuring the performance of a business within shorter time frames. These KPIs focus on the day-to-day operations and processes that contribute to overall success.
While strategic and functional unit KPIs provide broader insights, operational KPIs zoom in on specific areas such as order fulfillment time and time to market. It is important for these metrics to align directly with the organization’s goals and be SMART: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-bound.
Regularly reviewing and adapting operational KPIs is vital to keep up with changing business needs and customer expectations.
Customer KPIs
Customer KPIs are essential metrics that organizations use to assess their performance in relation to customer satisfaction and retention. These metrics provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of customer service efforts, allowing businesses to identify areas for improvement.
Customer KPIs can include measurements such as customer satisfaction scores, repeat purchase percentage, Net Promoter Score (NPS), and customer churn rate. By monitoring these key indicators, businesses can gain a better understanding of their customers’ preferences and needs, make data-driven decisions, and ultimately enhance their overall relationship with customers.
Creating Effective KPIs: How to Develop KPIs
Developing effective KPIs involves making them SMART (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time-bound), linking them to strategic goals, and balancing leading and lagging indicators.
Making KPIs SMART (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time-bound)
To ensure the effectiveness of KPIs, it is important to make them SMART:
- Specify clear and specific objectives for each KPI.
- Ensure that the KPIs are measurable and quantifiable, allowing for data – driven tracking and analysis.
- Set attainable goals that are realistic and within reach.
- Ensure that the KPIs are relevant to the overall business objectives and align with strategic goals.
- Establish a time frame or deadline for achieving the KPIs, providing a sense of urgency and focus.
Linking KPIs to strategic goals
KPIs play a critical role in linking strategic goals to performance measurement. By aligning KPIs with an organization’s strategic objectives, companies can track progress and make informed decisions that drive success.
When KPIs are directly tied to strategic goals, they provide clear targets and milestones for measuring progress towards desired outcomes. This alignment enables organizations to focus their efforts on areas that will have the greatest impact on achieving their long-term vision.
Regularly reviewing and iterating on KPIs is crucial to ensure that they remain relevant and aligned with changes in the market and within the organization itself. Ultimately, by linking KPIs to strategic goals, companies inspire action and create a culture of accountability where everyone is driven towards achieving shared objectives.
Balancing leading and lagging indicators
Balancing leading and lagging indicators is crucial for understanding performance and making informed decisions. Leading indicators are predictive in nature, offering early warning signs that allow proactive planning.
On the other hand, lagging indicators provide historical data that can be analyzed to gain insights into past performance. To have a comprehensive view of performance, effective KPIs should include a mix of both types.
This balance enables real-time monitoring of performance and allows for adjustments to strategies as needed. By considering both leading and lagging indicators, organizations can stay ahead of potential issues while also learning from past experiences.
The Power of KPIs: Benefits of Utilizing KPIs
Utilizing KPIs offers several benefits, including improving employee engagement, connecting organizational purpose and culture, and enhancing accountability for performance.
Improving employee engagement
Improving employee engagement is crucial for any organization’s success. Engaged employees are more motivated, productive, and committed to their work. They have a sense of purpose and connection with the organization, leading to higher job satisfaction.
When employees are engaged, they are more likely to go above and beyond their job responsibilities, contributing positively to the company’s overall performance.
One way to improve employee engagement is by providing opportunities for professional development and growth. Investing in training programs or offering career advancement paths can help employees feel valued and empowered in their roles.
Additionally, creating a supportive work environment that fosters open communication, recognition of achievements, and collaboration can contribute to increased engagement levels among employees.
Connecting organizational purpose and culture
Organizational purpose and culture are critical elements that shape the identity and values of a company. KPIs play a vital role in connecting these two aspects by aligning employee performance with the overall mission and values of the organization.
When employees have a clear understanding of their role in achieving strategic goals, it creates a sense of purpose and direction within the company culture. By establishing KPIs that reflect these objectives, organizations can foster a strong connection between individual performance and the broader organizational purpose.
This not only improves employee engagement but also enhances accountability for driving results that are in line with the desired culture.
Enhancing accountability for performance
KPIs play a vital role in enhancing accountability for performance. By setting specific targets and milestones, KPIs hold teams accountable for their actions and outcomes. They provide a clear framework for measuring progress and improvement, ensuring that everyone is working towards the same objectives.
KPIs also act as a health check for organizations, highlighting areas that need attention or where performance is lacking. With data visualizations and a KPI-focused culture, organizations can inspire action and drive continuous improvement based on measurable results.
Measuring Success: How to Measure KPIs
Measuring the success of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is crucial for monitoring progress and making informed decisions. To measure KPIs effectively, you need to establish clear metrics that align with your strategic goals.
This involves defining specific targets and milestones that can be quantified and tracked over time. By regularly collecting and analyzing data related to your KPIs, you can gain valuable insights into the performance of your organization or team.
This data-driven approach enables you to identify areas for improvement, make necessary adjustments, and optimize business outcomes. With a focus on measurable results, measuring KPIs empowers you to drive success and achieve continuous growth.
KPI Dashboards: The Essential Tool for Monitoring KPIs
KPI dashboards are crucial for monitoring KPIs as they provide real-time data visualizations and insights that help businesses make informed decisions and track progress towards their strategic goals.
Advantages of using KPI software
KPI software offers several advantages for organizations seeking to monitor and track their key performance indicators. Firstly, KPI software enables real-time monitoring, providing instant insights into the organization’s performance.
This allows teams to quickly identify any issues or areas that require attention. Secondly, KPI software centralizes data from various sources, making it easier to analyze and interpret information.
This eliminates the need for manual data gathering and ensures accuracy in reporting. Thirdly, KPI software offers scalability, allowing organizations to easily add or modify metrics as needed without disrupting operations.
Finally, utilizing KPI software increases efficiency by automating data visualization and reporting processes, saving time and resources that can be redirected towards driving business growth.
[FACTS]:
– KPI software enables real-time monitoring of an organization’s performance.
Steps to create a KPI Dashboard
To create a KPI Dashboard, follow these steps:
- Identify your organizational objectives and determine which key performance indicators (KPIs) align with them.
- Gather the necessary data from relevant sources and ensure it is accurate and up-to-date.
- Choose the appropriate data visualization tools and software to create your dashboard.
- Design the layout of your dashboard, including the placement of KPIs, graphs, and charts.
- Customize the dashboard to suit the needs of different users or departments within your organization.
- Set clear goals and targets for each KPI displayed on the dashboard.
- Regularly track and monitor the data, making adjustments as needed to optimize performance.
- Share the dashboard with relevant stakeholders, ensuring they understand how to interpret and use the information provided.
- Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of your dashboard and make improvements as necessary to meet changing business needs.
KPI Examples in Different Fields
KPI examples in different fields include finance, sales, marketing, IT, and customer service.
Finance
Finance KPIs are essential for monitoring the financial performance of a business and making informed decisions based on data. These indicators provide measurable metrics that help evaluate the success of financial activities.
Examples of finance KPIs include gross profit margin, net profit margin, and revenue growth. By tracking these KPIs, businesses can gain insights into their expenses, revenues, margins, and cash management.
This information is crucial for maintaining financial health and planning for future growth.
Customer service KPIs in finance focus on both short- and long-term targets related to customers, employees, and finances. These indicators help measure customer satisfaction levels, employee performance in handling financial queries or issues, as well as the overall effectiveness of customer support operations.
By monitoring customer service KPIs such as response time to inquiries or complaint resolution rates, businesses can ensure they are delivering quality services while also optimizing their financial processes.
Overall Finance KPIs play a critical role in ensuring the financial stability and success of a business by providing tangible metrics that allow companies to track progress towards financial goals while making data-driven decisions based on accurate information.
Sales
Sales KPIs play a crucial role in measuring the effectiveness and efficiency of sales efforts. They provide valuable insights into individual sales representatives, sales teams, and the overall performance of the sales organization.
By tracking metrics such as gross profit margin, net profit margin, new inbound leads, total pipeline value, net sales, and closed sales, businesses can optimize their sales strategies and evaluate the success of their initiatives.
Sales KPIs also help monitor revenue growth, customer acquisition costs, conversion rates, as well as analyze performance by region or product. With these key indicators at hand, businesses can make data-driven decisions to drive revenue and improve overall sales performance.
Marketing
Marketing is a crucial aspect of any business, and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) play a significant role in measuring marketing success. KPIs help companies track the effectiveness of their marketing strategies and make data-driven decisions.

By monitoring metrics such as customer acquisition cost, return on ad spend, and conversion rates, businesses can identify areas for improvement and optimize their marketing efforts.
With the right marketing KPIs in place, organizations can align their teams, hold them accountable for results, and create a culture of continuous improvement. Ultimately, leveraging KPIs in marketing enables companies to drive better business outcomes and stay ahead of the competition.
IT
IT plays a crucial role in organizations, and measuring its performance is essential for optimal functioning. IT Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) allow businesses to assess the effectiveness of their IT systems and processes.
These KPIs focus on outcomes such as system uptime, response time, and customer satisfaction. By tracking leading and lagging indicators, organizations can predict future outcomes and make data-driven decisions to improve IT performance.
Aligning IT KPIs with business objectives and ensuring they are measurable and actionable are best practices in developing effective measures for IT success. With the help of data visualization tools and a strong KPI strategy, organizations can monitor their IT systems closely, identify areas for improvement, and optimize overall performance.
Customer Service
Customer service is a crucial aspect of any business, and measuring its performance through key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential. Customer service KPIs focus on various aspects such as customer satisfaction, employee performance, and financial outcomes.
For example, net promoter score (NPS) and customer effort score are common KPIs used to assess customer satisfaction. Regularly reviewing and adjusting these KPIs ensures they remain relevant and aligned with the organization’s goals.
Additionally, data literacy plays an important role in understanding and acting on customer service KPIs. By utilizing effective customer service KPIs, organizations can inspire action and create a culture that prioritizes excellent customer support.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding key performance indicators (KPIs) is crucial for organizations to track progress and make informed decisions. By setting specific targets and measuring performance against them, KPIs help drive results and hold teams accountable.
With the right KPIs in place, businesses can optimize their performance and achieve their strategic goals.

