Mastering Tax Management: Essential Tips for Remote Social Media Workers
Are you a remote social media worker wondering about the tax implications? Here’s a fact – your taxes may differ significantly from traditional employees due to various aspects such as location and employment type.
This blog post will guide you through essential tips and tricks to navigate your tax landscape effectively, ensuring that you’re neither underpaying nor overpaying. Stay with us for valuable insights to make this taxing issue uncomplicated!
Key Takeaways
- Remote social media workers may have different tax obligations compared to traditional employees due to factors such as location and employment type.
- Understanding location – based taxation is crucial for remote workers, as taxes are based on where work is performed, not just where they live.
- Remote workers should engage tax professionals, maintain accurate documentation, and stay informed about international work dynamics to effectively manage their taxes.
Understanding Remote Work and Taxes
Remote work has significant implications for income taxes, as it can impact the tax obligations of individuals based on their location and employment type.
How Remote Work Affects Income Taxes
Working remotely can significantly impact your income taxes in ways you might not expect. For instance, if you’re a full-time employee who’s switched to telecommuting, your tax obligations largely stay the same.
However, there might be changes regarding deductions for home office expenses and work-related tools or software. Additionally, remote workers being paid by companies outside their state of residence may need to file income taxes in two states due to differing state tax laws.
A scenario floods up when some states impose the “convenience of the employer” rule leading to double taxation – both at the employer’s state and yours. Other considerations include city or county taxes that remote workers may have based on where they live and where their company is headquartered.
Therefore, understanding these complexities is crucial for predicting financial bills accurately during tax season.
The Impact of Location on Taxes for Remote Workers
The location of remote workers significantly influences the amount of taxes they pay. A remote worker living and working in New York, for instance, has different tax obligations than a similar professional residing in Texas.
This is largely due to varying state income tax laws across the U.S., with some states imposing higher taxes than others. Additionally, international remote work introduces even more complexities into this equation.
Different countries have their own unique tax codes and agreements affecting U.S citizens working abroad. Therefore, understanding these diverse regulations and policies crucially shapes your tax liabilities as a digital nomad or an overseas employee.
Conversely, if you’re a full-time employee or independent contractor, familiarize yourself with potential work-related deductions available to lighten your financial burden during the tax season.
Tax Implications for Remote Social Media Workers
Remote social media workers need to be aware of location-based taxation and understand the specific tax implications based on their employment type, whether they are independent contractors, full-time employees, or small business owners.
Location-Based Taxation
Location-based taxation dictates that you’re taxed according to where your work is performed, not just where you live. This particularly affects remote workers as they often execute tasks in a different location than their employer’s headquarters.
With the advent of digital nomads and overseas employment, understanding tax rules from both sides becomes critical.
U.S citizens working abroad must be mindful of the tax treaties between the U.S and other nations. These agreements help prevent double taxation by outlining which country has the right to apply taxes on certain types of income.
Therefore, it’s imperative for remote workers to familiarize themselves with local regulations in order to comply accurately with their tax obligations.
Tax Implications by Employment Type
The tax obligations of remote social media workers vary greatly based on their employment type. Below is a table that breaks down some of these differences:
Accuracy in documentation of work-related transactions and expenses becomes vital for all remote workers during tax season. Independent contractors especially need to ensure maintaining accurate records to avail of their wider range of deductions and tax credits.
How State and Federal Taxes Apply to Remote Workers
State and federal taxes apply to remote workers, presenting a dual challenge in terms of tax obligations due to the location-based nature of taxation and the potential impact on state and local income taxes.
The Dual Challenge of State and Federal Taxes
Remote workers face a dual challenge when it comes to state and federal taxes. Unlike traditional employees, remote workers may have tax obligations in multiple states or even countries.
This means they must navigate the complexities of both state and federal tax laws, ensuring compliance with each jurisdiction’s requirements. It can be a daunting task to determine which rules apply, calculate the appropriate taxes owed, and file accurate returns.
Remote workers need to understand the specific tax implications that come with their work arrangement and ensure they are prepared to address both state and federal tax obligations accordingly.
How Remote Work Can Affect State and Local Income Taxes
Remote work can have significant implications for state and local income taxes. Depending on where you live and the rules of your state, remote workers may be subject to taxation in multiple jurisdictions.
For example, some states have a “convenience of the employer” rule, which means that if you work remotely for a company based in another state, you may be required to pay taxes in both your home state and the state where your employer is located.
Additionally, remote workers may also have tax liabilities for city or county taxes in their place of residence and their employer’s location. It’s important for remote workers to review the tax laws of their state, as well as any applicable city or county regulations, to ensure compliance and avoid any surprises come tax season.
Essential Tax Information for Remote Workers
Remote workers must understand tax identification and the role of a Tax Identification Number (TIN) to ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Understanding Tax Identification
Tax identification is an important concept for remote workers to understand. It refers to the unique identification number assigned by a tax authority, such as the IRS in the United States.
This number, often called a Tax Identification Number (TIN), is used to track and record an individual or business’s tax obligations. It helps to ensure that taxes are accurately reported and paid.
As a remote worker, it’s essential to have a TIN and provide it when necessary for tax purposes. This helps both you and the tax authorities stay compliant with tax laws and regulations.
Remote workers may need different types of TINs depending on their employment status or business structure. For example, self-employed individuals typically use a Social Security Number (SSN) or an Employer Identification Number (EIN).
The Role of Tax Identification Number (TIN)
Every country has its own tax identification system, and having the correct Tax Identification Number (TIN) is important for accurate tax reporting. The TIN serves as a unique identifier that helps tax authorities track and verify taxpayers’ information.
It is used when filing tax returns, claiming deductions, and receiving credits or refunds. Whether you are a remote social media worker based in the US or working internationally, obtaining the correct TIN ensures compliance with local regulations and facilitates smooth processing of your taxes.
Tips for Managing Taxes as a Remote Worker
Engage tax professionals, maintain accurate documentation, and understand international work dynamics.
Engaging Tax Professionals
Engaging tax professionals can be a smart move for remote social media workers. Tax rules and regulations can be complex, especially when you’re juggling multiple jurisdictions and employment types.
Tax professionals are well-versed in navigating these complexities and can help ensure that you comply with all the necessary tax laws while maximizing your deductions. With their expertise, they can provide valuable guidance on issues like location-based taxation, international work dynamics, and state versus federal taxes.
By working with a tax professional, you can save time, reduce stress, and potentially even lower your overall tax burden.
Maintaining Accurate Documentation
Remote workers must prioritize maintaining accurate documentation to ensure compliance with tax regulations. Keeping organized records of income, expenses, and deductions is essential for accurately reporting taxes and minimizing the risk of audits or penalties.
Accurate documentation includes invoices, receipts, bank statements, and any other relevant financial records. By diligently tracking these documents throughout the year, remote workers can easily prepare their tax returns and provide necessary evidence if required by tax authorities.
Maintaining accurate documentation also helps in claiming eligible deductions and credits, maximizing potential tax savings. Proactive record-keeping not only simplifies the tax filing process but also enhances financial transparency and accountability for remote workers who are responsible for managing their own taxes.
Understanding International Work Dynamics
Remote workers must understand the international work dynamics to effectively manage their taxes. Here are some key points to consider:
- Research tax treaties: U.S. citizens working abroad should familiarize themselves with tax treaties between the U.S. and other countries. These agreements can help determine how income is taxed and if any exemptions or credits apply.
- Know local regulations: Different countries have varying tax policies and regulations. Remote workers must comply with local tax laws, including reporting requirements and deadlines.
- Document work-related transactions: Maintaining accurate documentation of work-related expenses and income is crucial for remote workers. This includes invoices, receipts, and any other relevant financial records.
- Consider healthcare contributions: Depending on the country of residence, remote workers may need to contribute to social security or healthcare systems. Understanding these obligations will help ensure compliance.
- Consult a tax professional: Engaging the services of a tax professional or consultant can provide valuable insights and guidance for navigating international tax obligations as a remote worker.
Reducing Tax Burden for Remote Workers
Remote workers can take advantage of various strategies and deductions to minimize their tax burden, such as exploring tax credits, making contributions beyond taxes, and understanding the implications of international work dynamics.
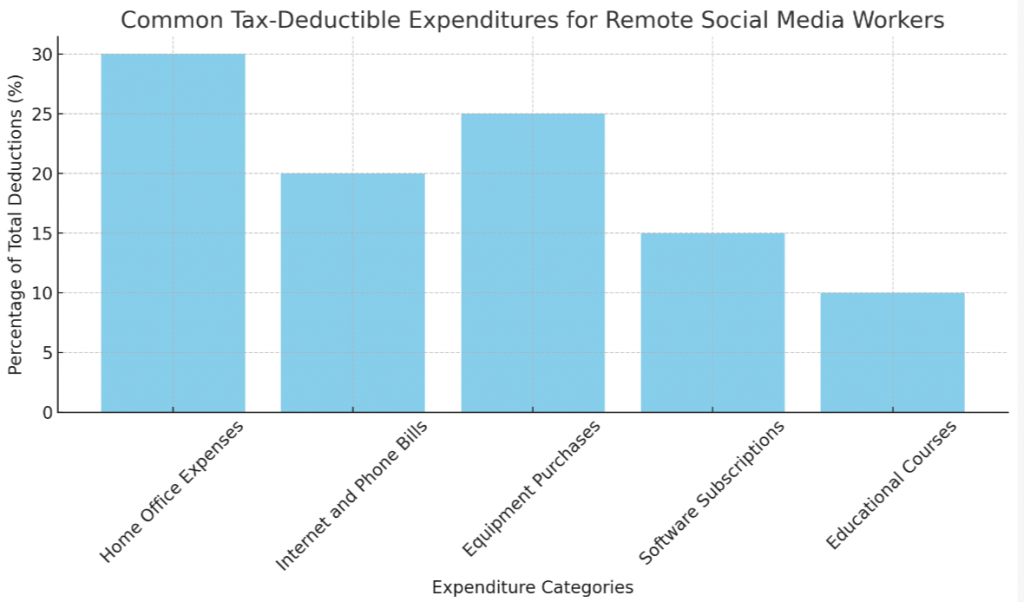
How Remote Workers Can Pay Less in Taxes
Remote workers have the opportunity to pay less in taxes by taking advantage of various strategies. One effective method is to maximize deductions and credits available for remote work expenses, such as home office costs or work-related travel expenses.
Remote workers should maintain accurate documentation to support these deductions and consult with a tax professional for guidance. Another way to reduce tax burden is by exploring contributions beyond taxes, such as contributing to retirement savings accounts that offer tax benefits.
By understanding the tax landscape and implementing smart strategies, remote workers can make the most of their financial situation and minimize their tax liabilities.
Contributions Beyond Tax
Remote social media workers have the opportunity to make contributions beyond their tax obligations. By being self-employed or running a small business, they can contribute to Social Security and healthcare programs.
These contributions ensure that remote workers have access to benefits like Medicare and other healthcare services in the future. Additionally, by paying into Social Security, they are building up their retirement savings for later years.
So, while managing taxes is important, remote social media workers should also consider the long-term benefits of these contributions that go beyond just fulfilling their tax duties.
Contributing to society goes beyond just paying taxes. Remote social media workers can use their skills and expertise to make an impact in their communities. They can volunteer or support nonprofit organizations through donations or pro bono work.
FAQs
Do I have to pay taxes in both the UK and the US if I work remotely for a US company from the UK? Can I live in another country and still work remotely for a US company?
Will I be taxed in UK or US if I work remotely for a US company from the UK?
If you work remotely for a US company from the UK, you may be subject to taxes in both countries. As a US citizen, you are required to report your global income to the IRS, which means you still need to file and pay taxes in the US.
However, since you are physically located in the UK while working, you will also have tax obligations there. It’s important to understand the tax laws of both countries and any potential tax treaties that may exist between them to determine how your income will be taxed.
Can you live in another country and work remotely at a US company?
Living in another country and working remotely for a US company is entirely possible. With the rise of remote work, many companies are embracing the idea of hiring employees from different parts of the world.
As long as you have a stable internet connection and can fulfill your job responsibilities, you can be employed by a US company while living abroad. This arrangement allows individuals to enjoy the benefits of living in another country while still earning income from their US employer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, remote social media workers face unique tax considerations due to the nature of their work. Understanding location-based taxation and the tax implications based on employment type is crucial for managing taxes effectively.
By seeking professional advice, maintaining accurate documentation, and staying informed about tax laws in their state of residence and employer’s location, remote workers can navigate the complexities of taxation and minimize their tax burden.

