Mastering Tax Compliance as a Remote Social Media Worker
Navigating the landscape of taxes for remote social media workers can be a daunting task. Did you know that your tax obligations can vary depending on whether you’re a full-time employee, contractor or sole proprietor? This comprehensive guide will demystify the complex world of taxation and simplify it to help you handle these responsibilities with confidence.
Stay tuned as we delve into some crucial tips that every remote worker should be aware of!
Key Takeaways
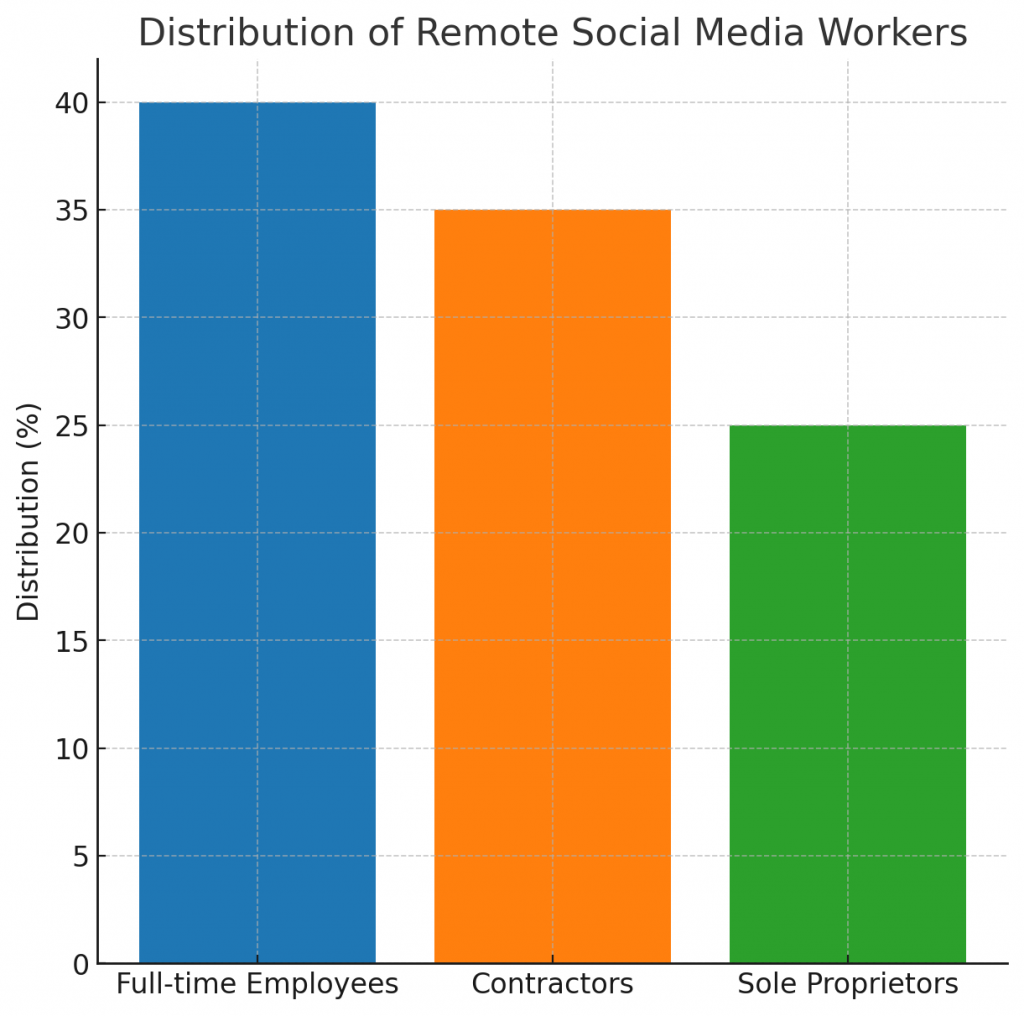
- Remote social media workers can fall into three categories: full-time employees, contractors, or sole proprietors. Each category has different tax obligations and benefits.
- Payment methods for remote workers vary depending on whether they are based in the U.S. or internationally.
- Remote workers need to understand the tax implications based on their location, such as same state, different states, or another country.
- To simplify taxes and payroll for remote workers, small business owners can use tax and payroll software, consult with financial consultants or tax preparation services, take advantage of available deductions and credits, stay informed about changes in tax laws, and consider partnering with a Global Employer of Record (EoR) like Velocity Global for international remote workers.
- Understand your tax obligations based on your employment status as a remote worker.
- Know the payment methods available for both U.S. – based and international remote workers.
- Familiarize yourself with the specific tax implications related to your location as a remote worker.
- Simplify taxes and payroll by using technology tools, seeking professional guidance when needed, staying updated on relevant laws, and exploring partnerships with global employment organizations.for international workers
Types of Remote Social Media Workers
There are three main types of remote social media workers: full-time employees, contractors, and sole proprietors.
Full-time Employees
Full-time employees are integral to small business operations, especially in the realm of remote social media work. These workers have a distinct tax status and benefits package. Unlike contractors or sole proprietors, full-time employees aren’t responsible for their own taxes.
Instead, their employers handle payroll deductions like federal income taxes and contributions to Social Security and Medicare. Depending on company policies, these employees may also qualify for perks such as health insurance and retirement plans including 401(k)s or SEP IRAs.
In terms of taxation rules, they follow the state laws where the employer is based. For instance, if both employee and employer reside in the same state, it’s generally expected that they file taxes there too.
Contractors
Contractors serve as an essential part of the remote workforce. These professionals typically handle their own taxes, which means they shoulder the responsibility for self-employment taxes and federal income taxes.
Unlike full-time employees who enjoy certain employee benefits like health insurance and retirement plans, contractors generally need to secure these necessities independently.
Being a contractor comes with unique tax implications that differ from other types of workers. State tax laws can vary widely in how they treat contractors, often depending on factors such as where the work is performed or the contractor’s official residence.
Contractors should be aware of potential double taxation situations if they live in one state but perform work in another.
Sole Proprietors
Sole proprietors, being self-employed individuals who run their own businesses, face distinct tax obligations. These business owners must shoulder the responsibility of paying their own taxes independently, which includes handling self-employment taxes.
In line with state laws and regulations, they also are tasked to issue W-2 forms to remote employees if necessary. The unique status of sole proprietors within the domain of taxation underscores the importance for these small business owners to fully understand and manage their tax responsibilities effectively and accurately in order not to fall foul of compliance errors or encounter unexpected financial hurdles.
Understanding How to Pay Remote Workers
When it comes to paying remote workers, there are different options depending on whether they are based in the U.S. or international.
Payment for U.S. Based Workers
Small business owners have various methods to pay their U.S. based remote teams, such as direct deposit, paper checks, or online payment platforms like PayPal, Venmo, and Zelle. Federal and state taxes must be withheld from the salaries of full-time workers while independent contractors are responsible for paying their own taxes including self-employment taxes.
Companies also have a legal responsibility to contribute towards Social Security and Medicare on behalf of their full-time employees. Furthermore, these companies need to ensure compliance with all relevant state laws and regulations when remunerating remote workers in the U.S., which includes issuing W-2 forms at tax time.
Payment for International Workers
International remote workers may face different challenges when it comes to receiving payment. Unlike their U.S.-based counterparts who have options like direct deposit or paper checks, international workers often rely on international money transfer services or online payment platforms such as PayPal, Venmo, Zelle, or Transferwise.
These services can facilitate the transfer of funds across borders and help ensure secure and timely payments for international workers. It’s important for employers to consider the available payment options and choose a method that is convenient and reliable for both parties involved.
Tax Implications for Remote Workers
Remote workers need to understand the tax implications based on their location, whether they are working in the same state, a different state, or another country.
Taxes for Workers in the Same State
Remote workers based in the same state as their employer have to navigate state tax laws. They are required to file taxes in that specific state, just like any other worker physically present there.
Employers play a crucial role in this process by withholding and filing state taxes for remote workers who are based in the same state. It is important for both employers and employees to understand the tax obligations associated with remote work within the same state, ensuring compliance with local labor and tax laws.
Taxes for Workers in Different States
Remote workers who reside in different states may be subject to different tax laws and regulations. Each state has its own rules regarding income tax, and employees may need to file taxes in multiple states if they work remotely across state lines.
This can complicate the tax process, as workers must determine their taxable income for each state they worked in during the tax year. It’s important for remote workers to stay informed about the tax requirements of each state they work in to ensure compliance and avoid any potential penalties or fines.
Taxes for Workers in Another Country
Remote workers based in another country are subject to tax laws and regulations specific to that country. These tax obligations can vary greatly depending on the individual’s employment status, income level, and any existing treaties between their home country and the country they are working in.
It is crucial for remote workers to understand their tax responsibilities in order to avoid potential penalties or violations. Seeking professional advice or consulting with a tax expert knowledgeable in international taxation can help navigate these complexities and ensure compliance with all relevant laws and regulations.
Tips to Simplify Taxes and Payroll for Remote Workers
Small business owners can simplify taxes and payroll for remote workers by following these tips:
- Use tax and payroll software like OnPay, Gusto, or ADP Run to automate the process.
- Consult with financial consultants or tax preparation services to ensure compliance with tax laws.
- Take advantage of tax deductions and credits available for remote workers, such as home office expenses or healthcare tax credits.
- Stay informed about changes in tax laws in the US and international tax laws that may affect remote workers.
- Consider partnering with a Global Employer of Record (EoR) like Velocity Global to handle compliance and payroll for international remote workers.
Special Considerations for Remote Workers Abroad
Remote workers abroad face unique challenges when it comes to taxes, such as navigating international tax laws and understanding the implications of working in one country while living in another.
Working in One Country and Living in Another
Remote workers who choose to work in one country while living in another face unique considerations when it comes to taxes. This situation often arises for digital nomads or individuals who work remotely for companies based in different countries than their own.
The tax implications can vary depending on the specific countries involved, and it’s essential for remote workers to understand international tax laws and their obligations. Different tax residency rules, double taxation treaties, and potential tax relief options should be considered by those working abroad.
It’s crucial to navigate these complexities properly to ensure compliance with both home and host country tax laws.
Understanding International Tax Laws
International tax laws can be complex and challenging to navigate for businesses with remote workers. It is important to understand the implications and requirements when it comes to paying taxes for international employees.
Businesses must consider factors such as tax residency, double taxation treaties, withholding tax rates, and compliance with foreign tax regulations. International remote workers may also have limited options for payment, so it’s crucial to explore secure methods such as international money transfers or online payment platforms like PayPal or Transferwise.
Additionally, businesses should seek the help of financial consultants or tax preparation services familiar with international tax laws to ensure compliance and avoid any penalties or fines associated with non-compliance.
The Consequences of Not Paying Taxes While Working Remotely
Not paying taxes while working remotely can have serious consequences. First and foremost, remote workers in the US who fail to fulfill their tax obligations may face penalties imposed by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
These penalties can include fines, interest charges on unpaid taxes, and even criminal charges in severe cases of tax evasion or fraud. Additionally, not paying taxes can potentially lead to restrictions on international travel or re-entry into certain countries.
Failure to comply with tax laws may also result in double taxation if a worker’s home country has a tax treaty with the country where they are working remotely. Overall, it is crucial for remote workers to understand and meet their tax responsibilities to avoid these negative consequences and maintain compliance with local labor and tax laws.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the tax implications for remote social media workers is crucial. Whether you’re a full-time employee or a contractor, knowing how to pay your taxes and stay compliant with state and federal laws is essential.
Keep accurate records and seek professional guidance to maximize deductions and credits. Stay informed about changes in tax laws to ensure smooth financial operations as a remote worker.

